A window is an opening in a wall, typically covered with transparent or translucent material, that allows light to enter a building or structure and provides a view of the outside. Windows play a significant role in architecture, interior design, and the overall functionality of a space. They serve several important purposes:
Natural Light: Windows allow natural sunlight to enter indoor spaces, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day. This can create a more inviting and visually pleasing environment.
Ventilation: Windows provide a means for fresh air to circulate within a building. Opening windows can help regulate indoor air quality and temperature.
Visual Connection: Windows provide views of the external environment, allowing occupants to connect with the outside world and enjoy scenic views.
Aesthetic Appeal: Windows contribute to the overall design and aesthetics of a building. They can enhance the architecture and interior design, adding character and style.
Energy Efficiency: Well-designed windows can contribute to energy efficiency by allowing natural heat to warm space during colder months (passive solar heating) and providing ventilation for cooling during warmer months.
Sound Insulation: Windows can help to reduce outdoor noise, providing a quieter indoor environment.
Privacy: While windows provide views, they can also be equipped with various types of coverings, such as curtains, blinds, or frosted glass, to maintain privacy when desired.
Emergency Egress: Windows can serve as emergency exits in case of fire or other emergencies.
Windows come in various sizes, shapes, and styles, and they can be made from different materials, including glass, acrylic, or polycarbonate.
They can be fixed in place or designed to open and close, offering different degrees of functionality and versatility. The design and placement of windows are crucial considerations in architectural and interior design, as they impact the overall look and feel of a space and influence its interaction with natural elements.
Types of Windows
Certainly, there are various types of windows, each with its own design, functionality, and characteristics. Here are some common types of windows:
Single-Hung Windows:
These windows have two sashes (movable panels). The bottom sash can be raised to open the window, while the top sash remains fixed. 
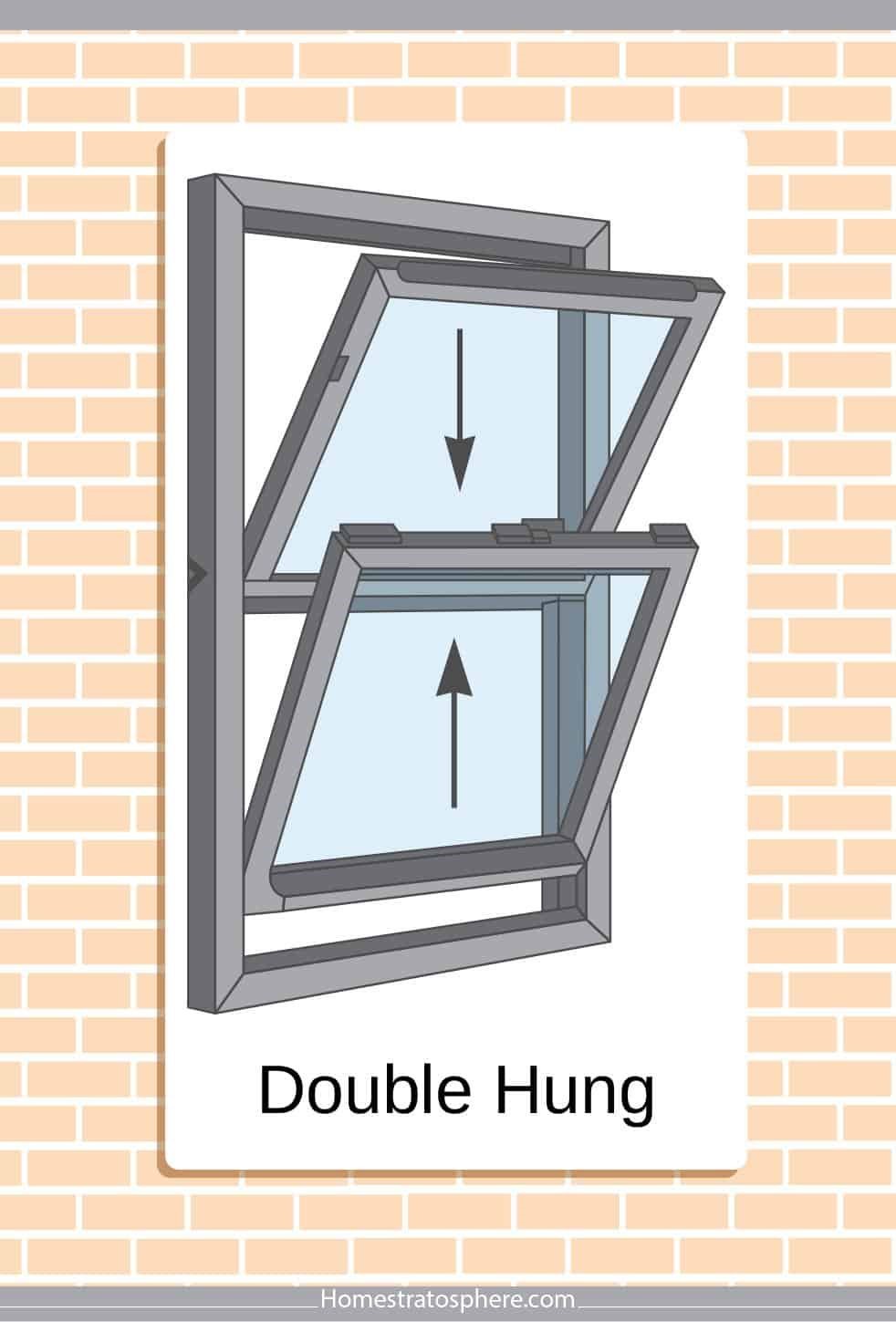
Double-Hung Windows:
Similar to single-hung windows, both the top and bottom sashes of double-hung windows can be moved. This allows for better control of ventilation.
Casement Windows:
Casement windows are hinged on one side and open outward like a door. They provide excellent ventilation and unobstructed views.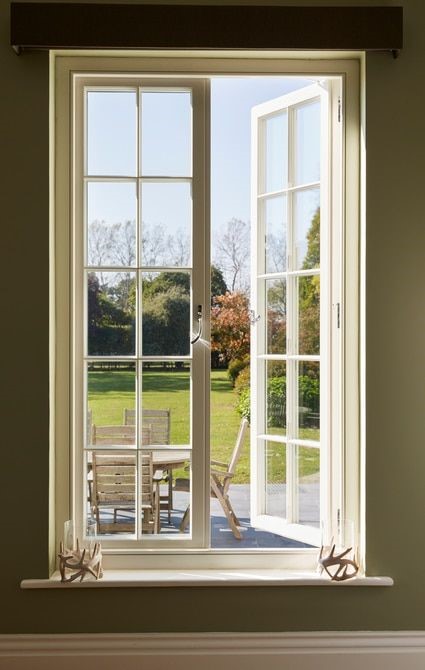 
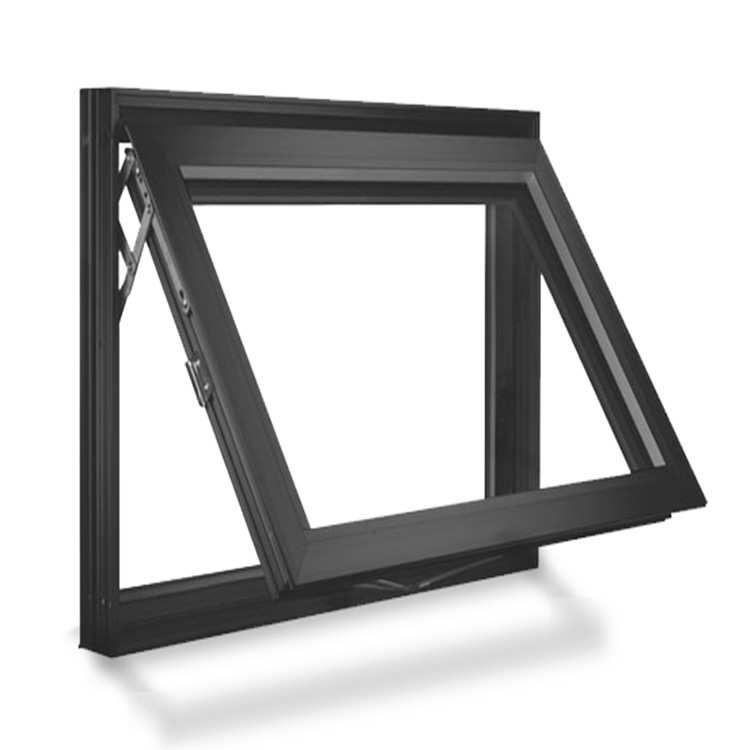
Awning Windows:
Awning windows are similar to casement windows but are hinged at the top. They open outward and create a small awning when open, which helps keep the rain out while allowing ventilation.

Slider Windows:
Slider windows have panels that slide horizontally along tracks. They provide easy operation and are often used in modern designs.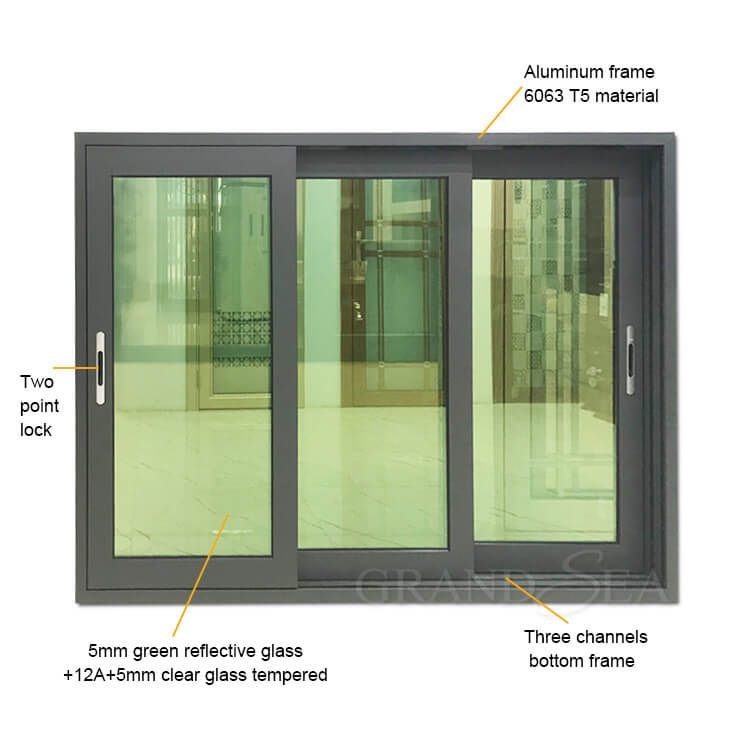 
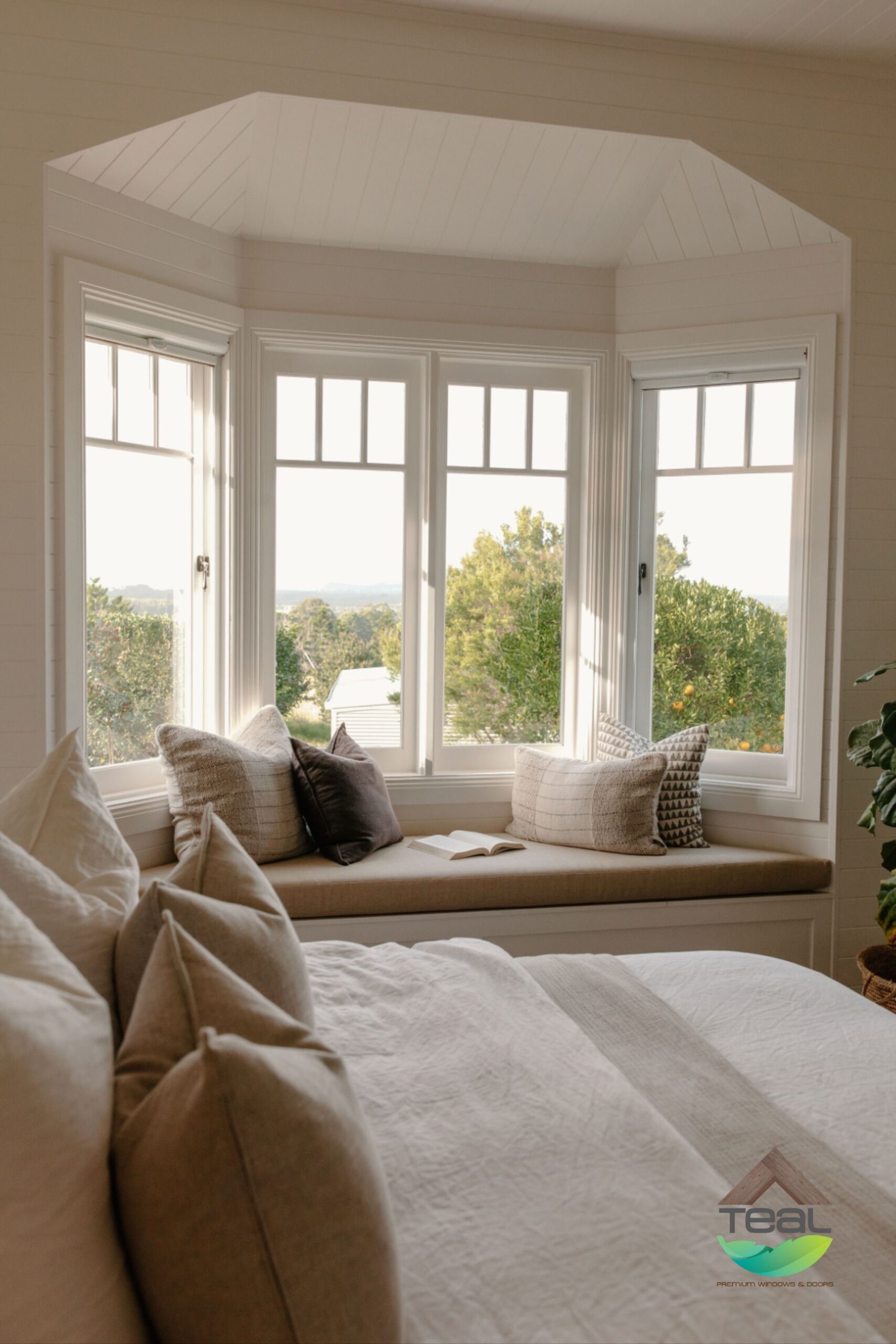
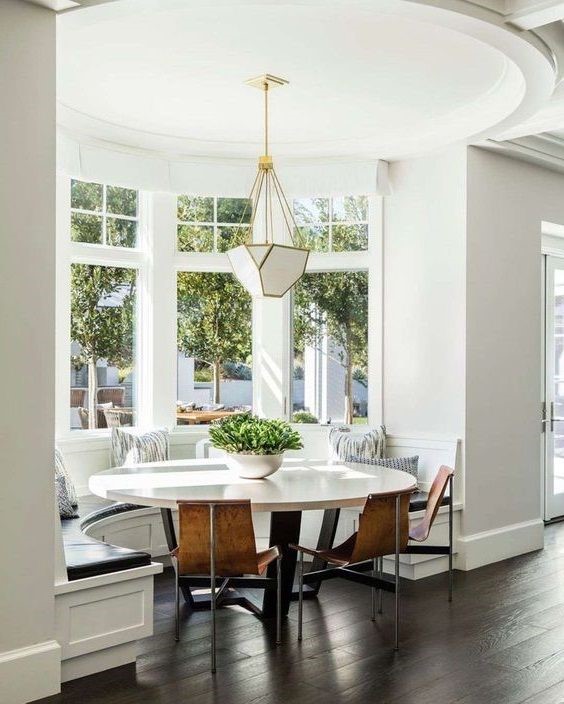
Bay Windows:
Bay windows are created by projecting outward from the building’s facade. They usually consist of three windows: a larger central one flanked by two smaller angled windows. Bay windows create a sense of space and can offer seating or display areas.

Bow Windows:
Similar to bay windows, bow windows are curved or rounded projections with multiple window panels. They often have a softer and more elegant appearance.

Picture Windows:
Picture windows are large, fixed windows that don’t open. They’re designed to frame outdoor views and let in abundant natural light.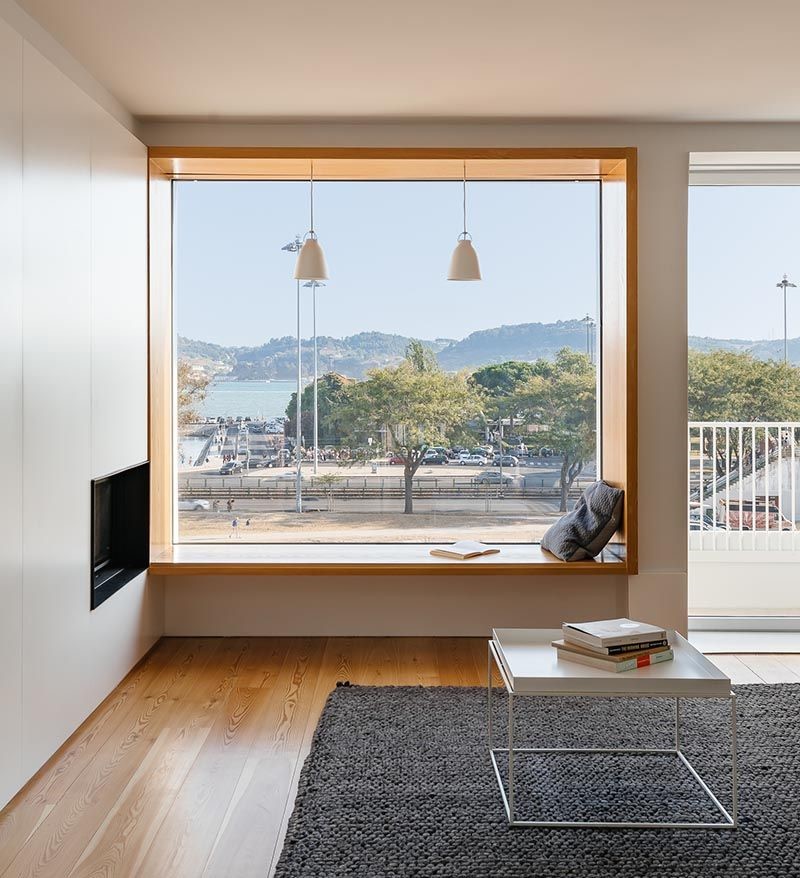 
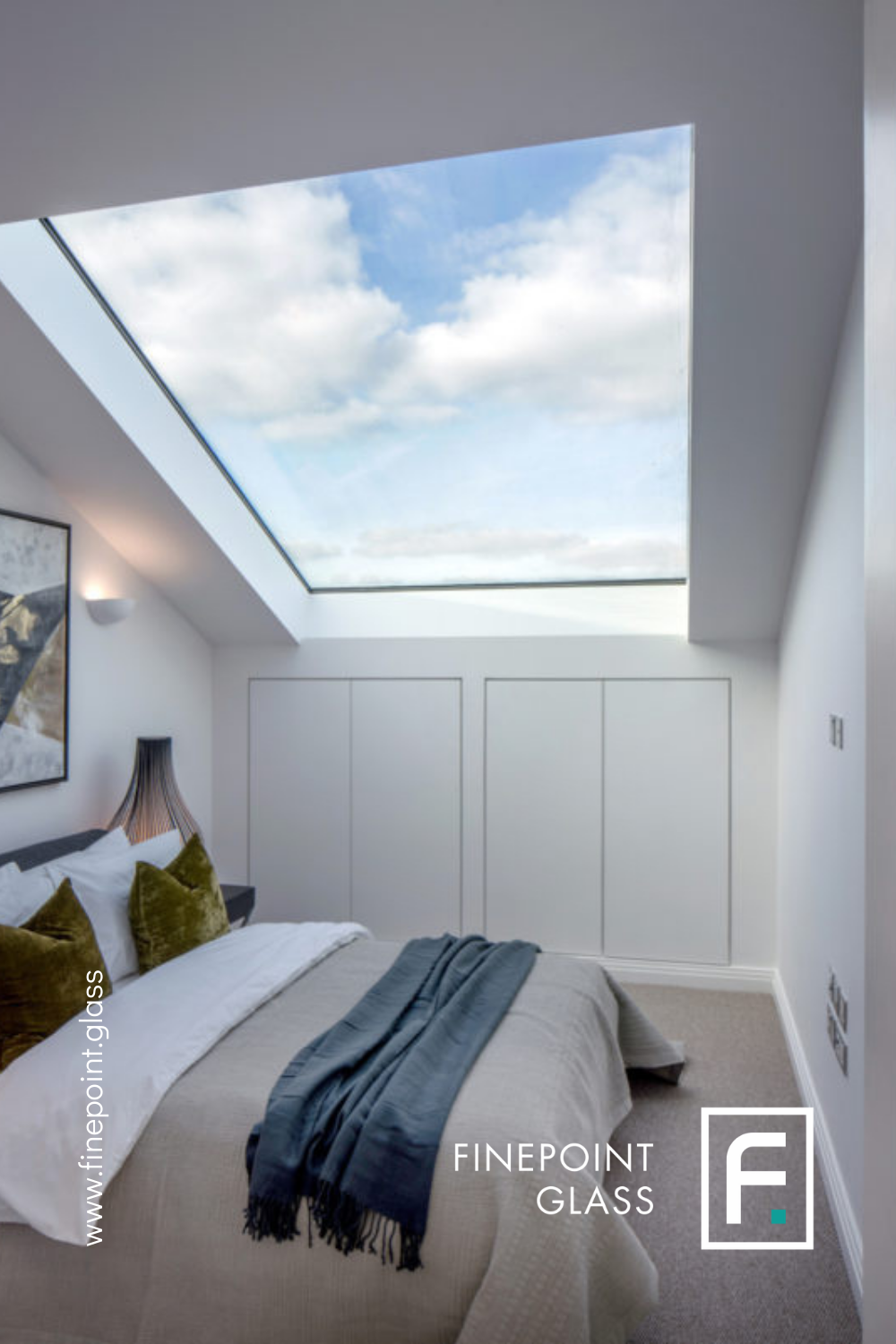
Skylights:
Skylights are windows installed on the roof or ceiling, allowing natural light to enter from above. They’re often used in areas with limited wall space.

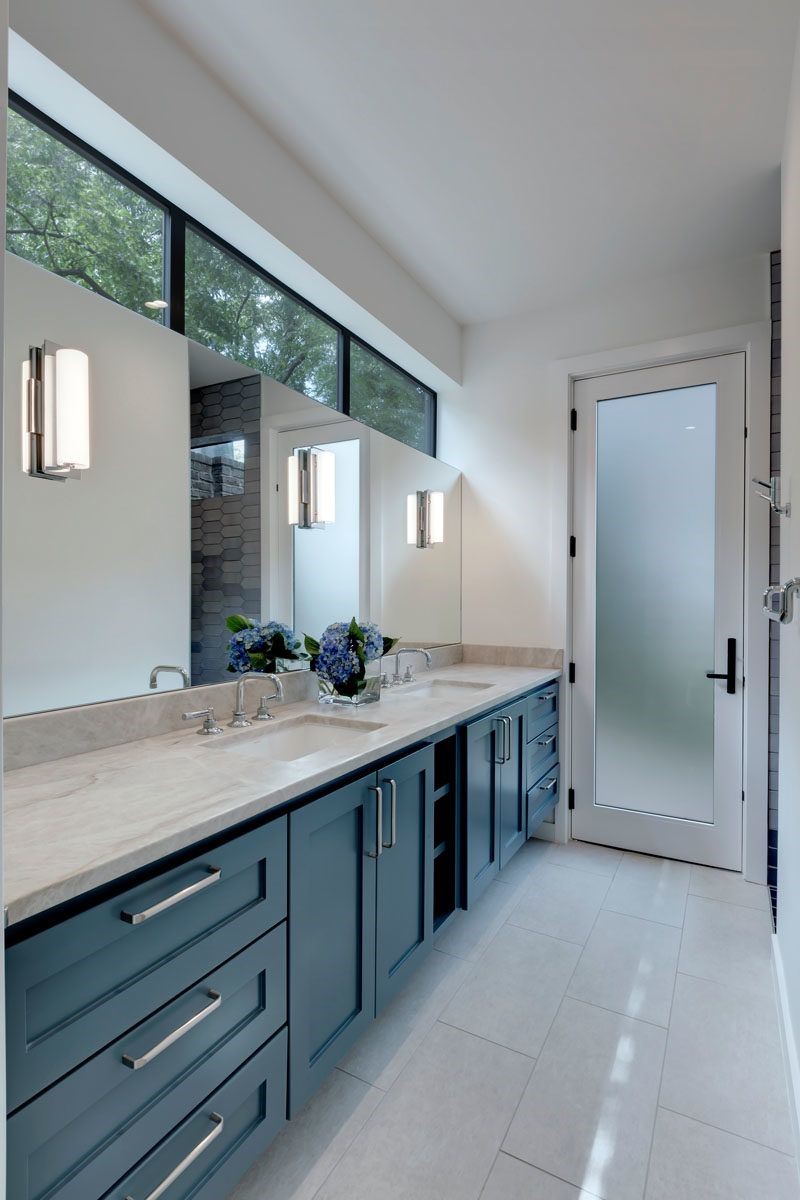
Clerestory Windows:
Clerestory windows are positioned high on a wall, near the ceiling. They provide light and privacy while maintaining wall space for other purposes.

Transom Windows:
Transom windows are located above doors or other windows to allow extra light and ventilation. They can be fixed or operable.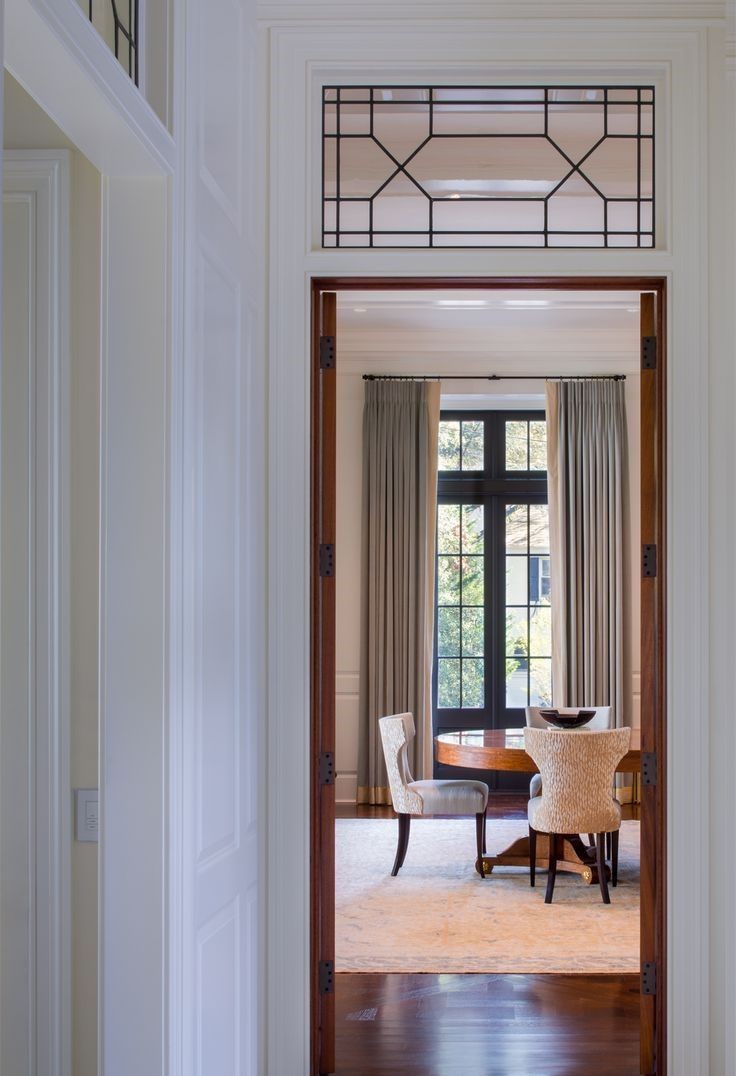 
Jalousie Windows:
Jalousie windows consist of parallel glass slats set in a metal or wooden frame. The slats can be opened and closed like blinds, providing adjustable ventilation.
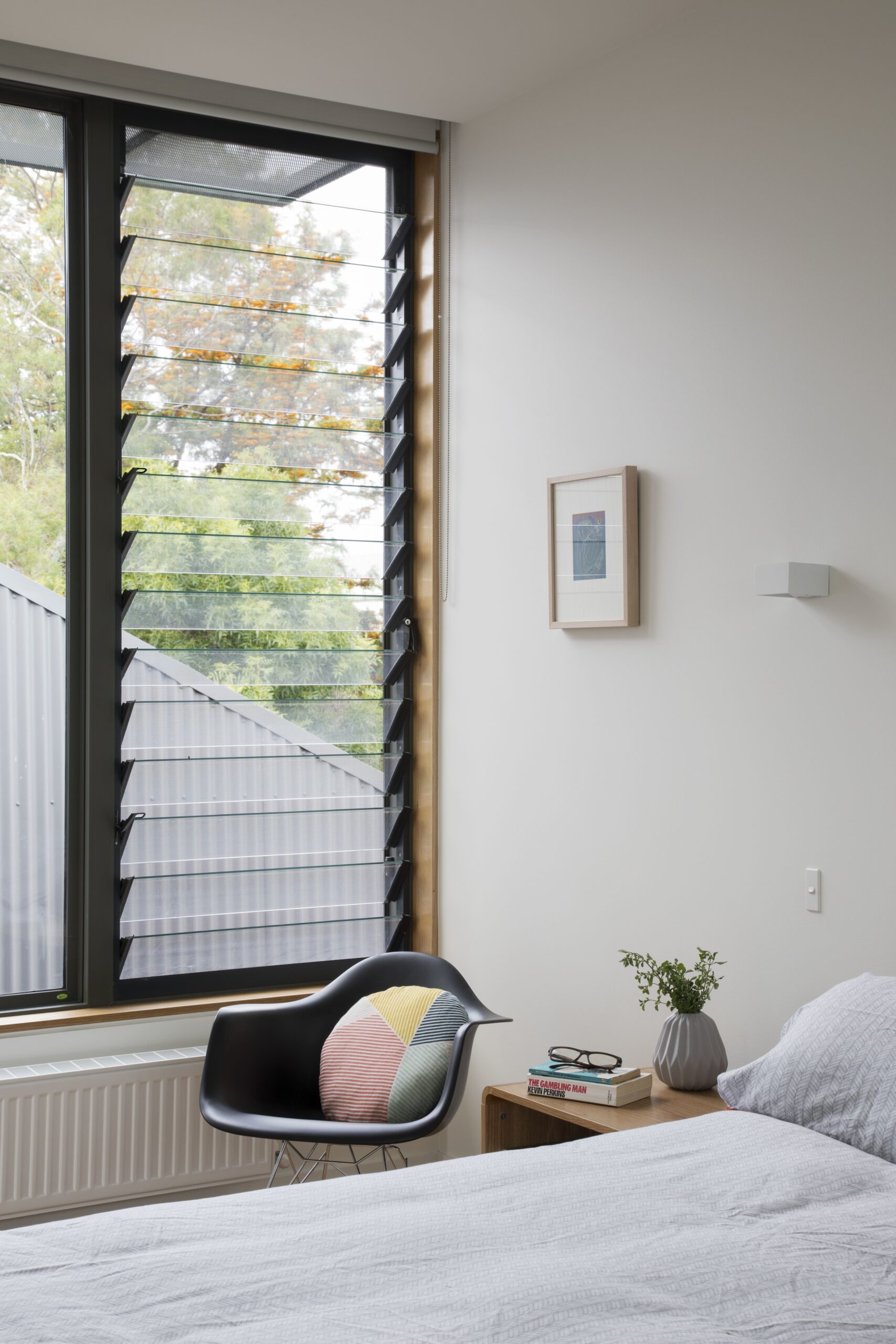

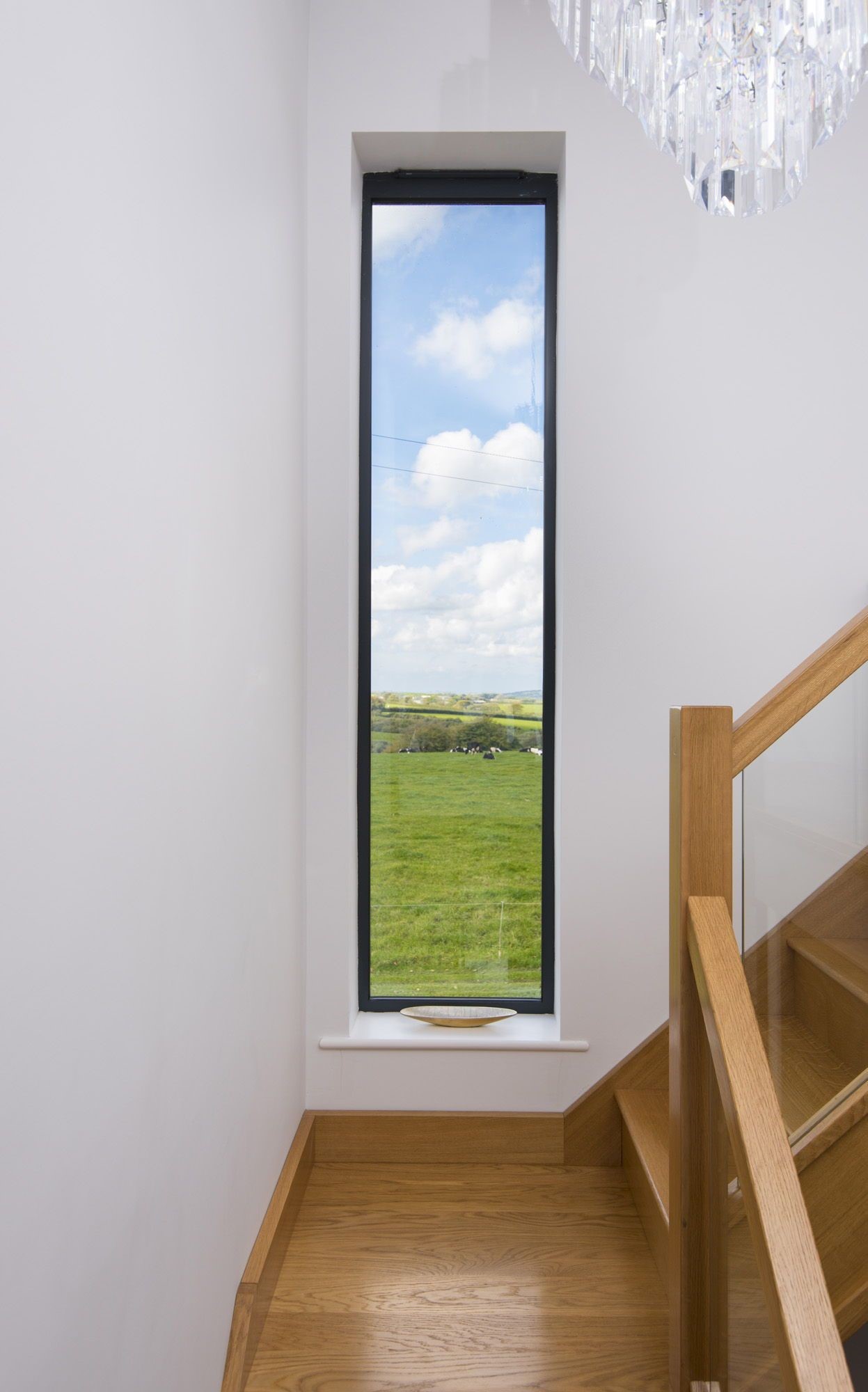
Fixed Windows:
Fixed windows are immovable and don’t open. They’re often used for decorative purposes, as part of larger window arrangements, or to enhance architecture.

Garden Windows:
Garden windows project outward like mini-bay windows. They’re often used in kitchens and are designed to hold plants or other decorative items.

These are just a few examples of the many types of windows available. The choice of window type depends on factors such as aesthetics, functionality, ventilation needs, and the architectural style of the building.

